Quinolone DNA complexes: Difference between revisions
(Cleaned up the page formatting, redid the numbering of the references and added links to the cited papers.) |
(Added an image of the structure of levofloxacin.) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Complexes of Quinolone Antibiotics and DNA == | == Complexes of Quinolone Antibiotics and DNA == | ||
Quinolone antibiotics are widely used in the clinic. They inhibit the re-sealing of the DNA after cleavage by a gyrase, thus turning a topoisomerase into a nuclease. Three-dimensional structures of covalent quinolone-DNA complexes have been elucidated by NMR and restrained molecular dynamics. | |||
[[File:Levofloxacin structure.png|right|thumb|Structure of levofloxacin, a prototypical quinolone antibiotic.]]Quinolone antibiotics are widely used in the clinic. They inhibit the re-sealing of the DNA after cleavage by a gyrase, thus turning a topoisomerase into a nuclease. Three-dimensional structures of covalent quinolone-DNA complexes have been elucidated by NMR and restrained molecular dynamics.<br><br><br><br><br><br><br> | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
Latest revision as of 14:17, 3 September 2024
Complexes of Quinolone Antibiotics and DNA
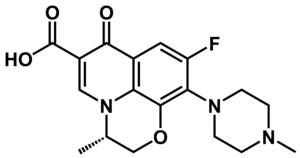
Quinolone antibiotics are widely used in the clinic. They inhibit the re-sealing of the DNA after cleavage by a gyrase, thus turning a topoisomerase into a nuclease. Three-dimensional structures of covalent quinolone-DNA complexes have been elucidated by NMR and restrained molecular dynamics.
References
[1] J. Tuma, W. H. Connors, D. H. Stitelman, C. Richert, On the Effect of Covalently Appended Quinolones on Termini of DNA-Duplexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 4236-4246. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja0125117
[2] K. Siegmund, S. Maheshwary, S. Narayanan, W. Connors, M. Riedrich, M. Printz, C. Richert, Molecular details of quinolone-DNA interactions: Solution structure of an unusually stable DNA duplex with covalently linked nalidixic acid residues and non-covalent complexes derived from it. Nucleic Acids Res., 2005, 33, 4838-4848. https://doi.org/10.1093%2Fnar%2Fgki795