Quinolone DNA complexes: Difference between revisions
(Created page with " '''Complexes of Quinolone Antibiotics and DNA''' Quinolone antibiotics are widely used in the clinic. They inhibit the re-sealing of the DNA after cleavage by a gyrase, thus turning a topoisomerase into a nuclease. Three-dimensional structures of covalent quinolone-DNA complexes have been elucidated by NMR and restrained molecular dynamics. '''References''' a) J. Tuma, W. H. Connors, D. H. Stitelman, C. Richert, On the Effect of Covalently Appended Quinolones on...") |
(Added an image of the structure of levofloxacin.) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Complexes of Quinolone Antibiotics and DNA == | |||
[[File:Levofloxacin structure.png|right|thumb|Structure of levofloxacin, a prototypical quinolone antibiotic.]]Quinolone antibiotics are widely used in the clinic. They inhibit the re-sealing of the DNA after cleavage by a gyrase, thus turning a topoisomerase into a nuclease. Three-dimensional structures of covalent quinolone-DNA complexes have been elucidated by NMR and restrained molecular dynamics.<br><br><br><br><br><br><br> | |||
''' | == References == | ||
[1] J. Tuma, W. H. Connors, D. H. Stitelman, C. Richert, On the Effect of Covalently Appended Quinolones on Termini of DNA-Duplexes. ''J. Am. Chem. Soc.'' '''2002''', ''124,'' 4236-4246. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja0125117 | |||
[2] K. Siegmund, S. Maheshwary, S. Narayanan, W. Connors, M. Riedrich, M. Printz, C. Richert, Molecular details of quinolone-DNA interactions: Solution structure of an unusually stable DNA duplex with covalently linked nalidixic acid residues and non-covalent complexes derived from it. ''Nucleic Acids Res.'', '''2005''', ''33'', 4838-4848. https://doi.org/10.1093%2Fnar%2Fgki795 | |||
Latest revision as of 14:17, 3 September 2024
Complexes of Quinolone Antibiotics and DNA
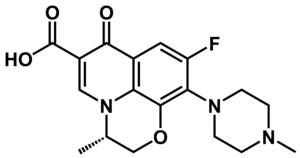
Quinolone antibiotics are widely used in the clinic. They inhibit the re-sealing of the DNA after cleavage by a gyrase, thus turning a topoisomerase into a nuclease. Three-dimensional structures of covalent quinolone-DNA complexes have been elucidated by NMR and restrained molecular dynamics.
References
[1] J. Tuma, W. H. Connors, D. H. Stitelman, C. Richert, On the Effect of Covalently Appended Quinolones on Termini of DNA-Duplexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 4236-4246. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja0125117
[2] K. Siegmund, S. Maheshwary, S. Narayanan, W. Connors, M. Riedrich, M. Printz, C. Richert, Molecular details of quinolone-DNA interactions: Solution structure of an unusually stable DNA duplex with covalently linked nalidixic acid residues and non-covalent complexes derived from it. Nucleic Acids Res., 2005, 33, 4838-4848. https://doi.org/10.1093%2Fnar%2Fgki795